Sections
- Influence of the state of the oceans on the planet’s balance
- Current situation of the oceans
- Actions to make the marine ecosystem sustainable
- Summary
The challenge of ocean pollution
In recent decades, marine pollution has established itself as one of the most urgent environmental challenges.
Every year, millions of tons of waste are dumped into the sea, seriously threatening biodiversity and the health of marine ecosystems.
This pressure is compounded by the increase in global temperatures, which directly affects the oceans’ ability to regulate the climate and absorb excess carbon dioxide.

These are the main challenges to be faced in the short term:
- Every year, millions of tons of waste, including plastics, are dumped into the seas, causing a destructive impact on marine life and ecosystems. Marine animals can mistake plastics for food, which can lead to malnutrition and, in many cases, death. Microplastics are small particles resulting from the breakdown of larger plastics, which have penetrated the marine food chain, affecting all species from plankton to large predators.
- Pollution also comes from toxic chemical substances such as pesticides, heavy metals, and pharmaceuticals that reach the oceans through rivers and urban discharges. These substances can cause mutations, diseases, and reduced fertility in marine life, profoundly altering ocean ecosystems.
- Oil spills are another example of pollution. Crude oil covers the bodies of marine animals and plants, preventing their ability to breathe, feed, and reproduce, resulting in high mortality rates.
- Massive antibiotic production causes medium- and long-term alterations in ecosystems.
- Overfishing, pollution, and climate change are reducing marine biodiversity and compromising the food security of millions of people.
- Destructive fishing practices, such as the use of trawl nets, also have devastating consequences. These nets not only catch large quantities of fish of all sizes but also devastate the seabed, destroying habitats such as reefs and seagrass meadows, which are essential for many species.
- Overfishing occurs when the rate at which certain fish populations are caught exceeds their capacity to reproduce. Overfishing not only affects the fish caught but also the entire ecosystem, as it disrupts the food chain and ecological balance.
- The increase in ocean water temperatures is affecting the migration cycles of many marine species and impacting their survival. Temperature changes directly affect corals, where marine species lose the symbiotic algae that provide them with food, risking massive die-offs.
Influence of the oceans on the planet’s balance
Ocean conservation is fundamental to preserving the planet’s ecological balance. This is how the oceans contribute to the planet’s balance:
- Oceans act as a thermal buffer, absorbing and distributing the heat provided by the sun through ocean currents. This process influences global climate patterns such as El Niño and La Niña, which directly affect the planet’s temperature and weather phenomena.
- Coral reefs, mangroves, and marshes help cushion the effects of high-intensity storms and hurricanes, protecting coastlines and reducing environmental impact.
- Oceans play a fundamental role in environmental balance by regulating the climate and absorbing carbon dioxide (approximately 30% of the carbon dioxide emitted by human activity). However, excess CO₂ causes water acidification, which affects marine organisms such as corals, mollusks, and plankton, which in turn can alter the rest of the marine ecosystems.
- Pollution and global warming threaten oxygen production in the oceans, which can pose a serious problem since much of the oxygen we breathe comes from marine organisms, especially from the photosynthesis of phytoplankton.
- Oceans also constitute the habitat of great biodiversity and are a vital source of food and resources for biological balance and human nutrition.
- On the other hand, oceans are the main agent of evaporation in the water cycle. This significantly affects meteorology and the availability of drinking water.
Current situation of the oceans
As mentioned, ocean ecosystems have been affected and altered due to increasing pollution.
The degradation of marine ecosystems, especially in coastal areas, has intensified considerably since the second half of the 20th century.
This situation is a direct consequence of the accumulation of waste, including wastewater generated by urban centers, agricultural and livestock activities, as well as discharges from industrial processes.
It is true that urban wastewater treatment plants have been built and environmental regulations regarding discharge limits have been tightened, but these treatment plants were designed to reduce the presence of the most basic contaminants, such as suspended solids, COD, oils, detergents, etc., so their effectiveness in eliminating emerging contaminants, including microcontaminants, is very limited.
These contaminants appear in very low concentrations (ppm, ppb) and are dangerous to the environment due to their toxicity. They originate from human activities such as agriculture (herbicides, pesticides, fertilizers), domestic discharges (garbage, pharmaceuticals, hygiene products, etc.), and industrial effluents such as cleaning products, solvents, degreasers, preservatives, fats, metals, etc.
The attached table shows the microcontaminants most frequently found in the environment, classified into groups based on their origin.
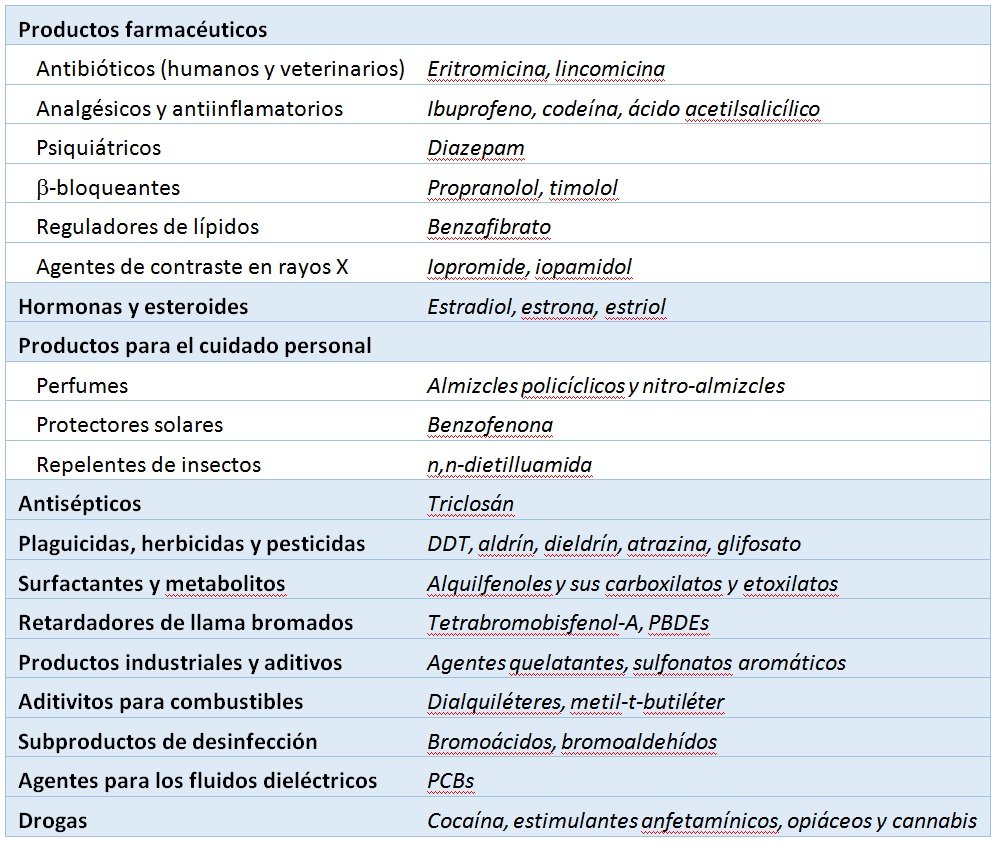
Table: Microcontaminants frequently found in the environment
Among the techniques used in microcontaminant treatment, those that have demonstrated the greatest effectiveness are:
- Filtration operations based on membrane use (UF/NF/RO)
- Advanced oxidation processes (ozonation and catalytic oxidation)
- Adsorption (using activated carbon and other absorbent materials)
Technology plays a vital role, offering innovative solutions to face these challenges and protect our seas.
Actions to maintain the sustainability of the marine ecosystem
Conservation and protection of the oceans constitute a global challenge in which both institutions and citizens have a key role to play.
Prevention is undoubtedly the most effective strategy: if we avoid pollution, we eliminate the need to correct its effects.
Therefore, it is essential to promote measures that help preserve the health of marine ecosystems, among which stand out:
- Avoid dumping chemical substances and toxic waste into the sea.
- Reduce plastic consumption and properly manage and dispose of it.
- Encourage sustainable marketing of seafood products.
- Use biodegradable products whenever possible.
- Do not leave waste or trash on beaches.
- Practice responsible navigation, complying with environmental regulations.
- Actively promote recycling and the circular economy.
Additionally, today we have technological tools and monitoring systems that allow us to assess the state of the oceans in real time and apply corrective measures more efficiently and precisely.
Some of the technologies applied are the following:
Satellites
They have become a valuable tool for monitoring the oceans. Thanks to satellites, scientists can collect precise data on various relevant factors to understand the evolution of the marine environment, such as:
- Sea surface temperature
- Salinity levels
- Chlorophyll concentration: Indicates the presence of phytoplankton, essential for the marine food chain.
- They detect areas of pollution and oil spills, allowing a quick and effective response to mitigate environmental damage.
- Observation of ocean circulation patterns and detection of many environmental phenomena.
In summary, satellites provide critical data that help guide conservation policies and mitigation strategies globally.
Underwater drones
Underwater drones are equipped with high-definition cameras, sensors, and sampling tools. These devices can operate at great depths and in conditions that would be impossible for humans.
They allow the collection of valuable data on marine biodiversity, ecosystem health, and underwater geology.
One of the most significant advantages of underwater drones is their ability to access remote and dangerous areas, such as ocean depths and polar regions.
Ocean cleanup
To separate contaminants present in seawater, two techniques are used that primarily aim to separate plastics:
- Plastic collecting ships are designed and equipped with advanced filtration and collection systems, capable of gathering large amounts of floating plastic. These ships use specialized nets and suction mechanisms that trap plastic without harming marine life. The collected plastics are then processed for recycling or proper disposal. In addition to collecting plastic, some of these ships are also equipped with sensors and monitoring equipment to study the concentration and impact of these materials in different oceanic areas.
- Floating barriers are installed in rivers, estuaries, and coasts to intercept plastics and other waste before they reach the open ocean. They are designed to be effective even in current and wave conditions, capturing large amounts of waste without interfering with marine life. By intercepting plastics at their source, it prevents them from breaking down into microplastics, which are much harder to eliminate.
Sustainable aquaculture

Sustainable aquaculture is a practice that ensures responsible fish production for human consumption. Sustainable aquaculture involves:
- Choosing appropriate species
- Using natural foods and supplements
- Implementing efficient waste management systems to avoid water pollution.
- Promoting the farming of native species instead of exotic species, which can become invasive if they escape into the environment
Through recirculating aquaculture systems, fish can be raised in tanks where water is continuously filtered and reused, reducing the need for fresh water and minimizing environmental impact.
They also reduce disease transmission and allow precise control of environmental conditions, ensuring the ability to produce fish year-round regardless of environmental conditions.
Conclusion
The oceans harbor an enormous variety of species that are essential for ecosystem stability and human nutrition.
The deterioration of the oceans due to pollution, global warming, and overexploitation has serious consequences for the planet’s balance. It is essential to adopt measures to reduce carbon emissions, protect marine biodiversity, and promote sustainable practices in the use of ocean resources.
Condorchem Enviro Solutions is an engineering company specialized in the development of plants for wastewater treatment. We help companies manage their wastewater effluents, ensuring safe water discharge for the environment and promoting water reuse systems.